Windsurf's SWE-1 model family - AI tools designed to enhance the entire software engineering lifecycle.
The SWE-1 model, launched by Windsurf, is a set of AI tools designed to enhance software engineering processes. This family includes three models, each tailored to different user needs and availability, aiming to revolutionize how software is developed.
These models are built to handle the entire software engineering lifecycle, not just coding, with features like "flow awareness" for seamless human-AI collaboration.
Development Acceleration
Reported potential acceleration when using SWE-1 models
The largest and most capable model, designed for advanced reasoning and tool use, available only to paid users.
A smaller but powerful model, replacing Windsurf's existing Cascade Base, available to all users, both free and paid.
A lightweight model for fast, passive code prediction, also available to all users, free and paid.

The frontier model family built for the full software engineering lifecycle.
SWE-1 models are built to handle the entire software engineering lifecycle, not just coding, with features like "flow awareness" for seamless human-AI collaboration.
Creates a shared timeline of actions between humans and AI, enabling continuous improvement.
Works across terminals, IDEs, and the internet for a cohesive experience.
Aims to accelerate development by up to 99%, reducing technical debt.
A detailed examination of the SWE-1 models, their features, availability, and impact.
Windsurf, previously known as Codeium, is a startup focused on AI tools for software engineers, particularly known for its "vibe coding" applications that allow code writing and editing through AI chatbots. On May 15, 2025, Windsurf announced the launch of its first family of in-house AI models, named SWE-1, as part of its Wave 9 update.
This launch coincides with reports of a potential $3 billion acquisition by OpenAI, though the deal is not yet closed, and Windsurf has not publicly commented on it.
The SWE-1 models are built through extensive in-house training with a new data model using sequential steps, specifically tailored for software engineering tasks. They are designed to support multiple surfaces, such as terminals, IDEs, and the internet, and handle incomplete work states and long-running tasks, which are critical in real-world development scenarios.
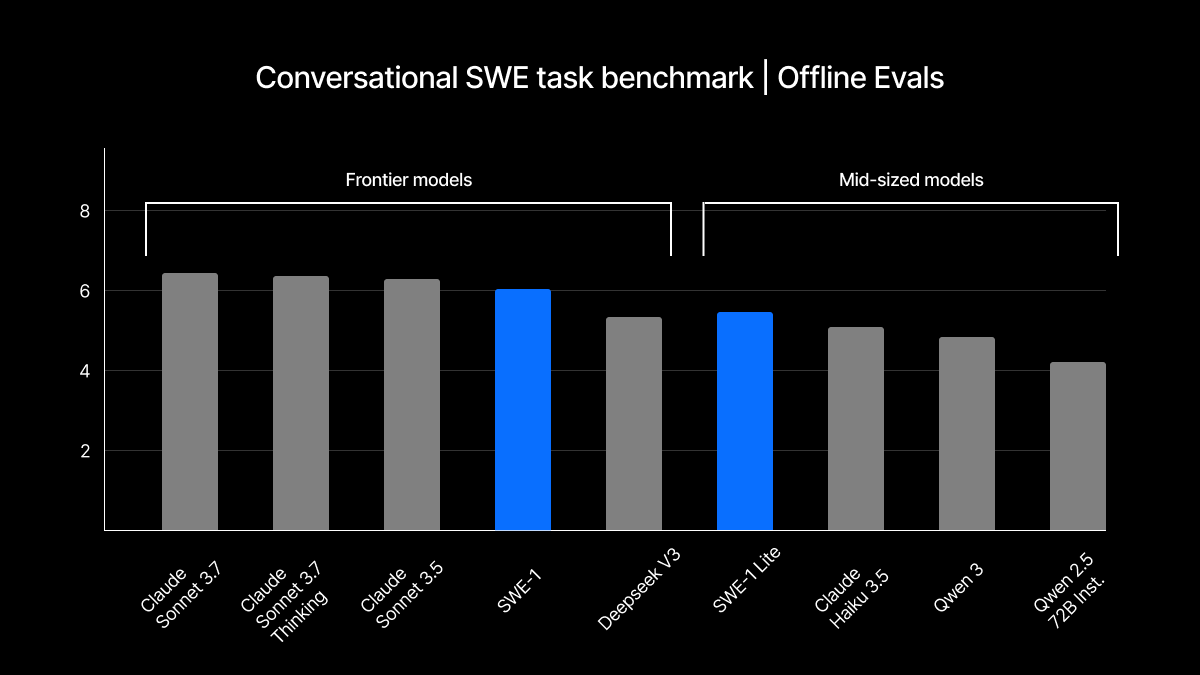
SWE-1 performance comparison on software engineering benchmarks
A key feature is "flow awareness," which creates a shared timeline of actions between humans and AI, enabling continuous improvement and progressive task transfer from human to AI. This feature is intended to keep developers in a "flow state," anticipating needs and resolving issues before they arise.
Performance-wise, SWE-1 is claimed to perform competitively with leading AI models like Claude 3.5 Sonnet, GPT-4.1, and Gemini 2.5 Pro on internal programming benchmarks, though it falls short of Claude 3.7 Sonnet for software engineering tasks.
Availability varies by model, with SWE-1 restricted to paid users, while SWE-1-lite and SWE-1-mini are accessible to all, both free and paid, with unlimited use. Pricing for SWE-1 was not immediately announced, but it is claimed to be cheaper to serve than Claude 3.5 Sonnet, potentially making it an attractive option for enterprises.
The SWE-1 models aim to accelerate software development by up to 99%, a bold claim supported by Windsurf's focus on addressing the entire engineering lifecycle, not just code generation. This is particularly significant in the context of reducing development cycles and technical debt.
The models' ability to reason over ambiguous and incomplete states underscores their potential to transform how software is built.
Get answers to common questions about SWE-1 model family and its capabilities.